Help documentation
Explore the official Rootlenses documentation and learn how to take full advantage of our suite of AI-powered solutions.Agents
1. Agent Management — Overview
What it's for
The Agents section allows you to manage the phone/virtual agents that run call campaigns: create new agents, configure their behavior, design contact sources, control schedules, define wait times, and review results and metrics.
What the customer will find in this area
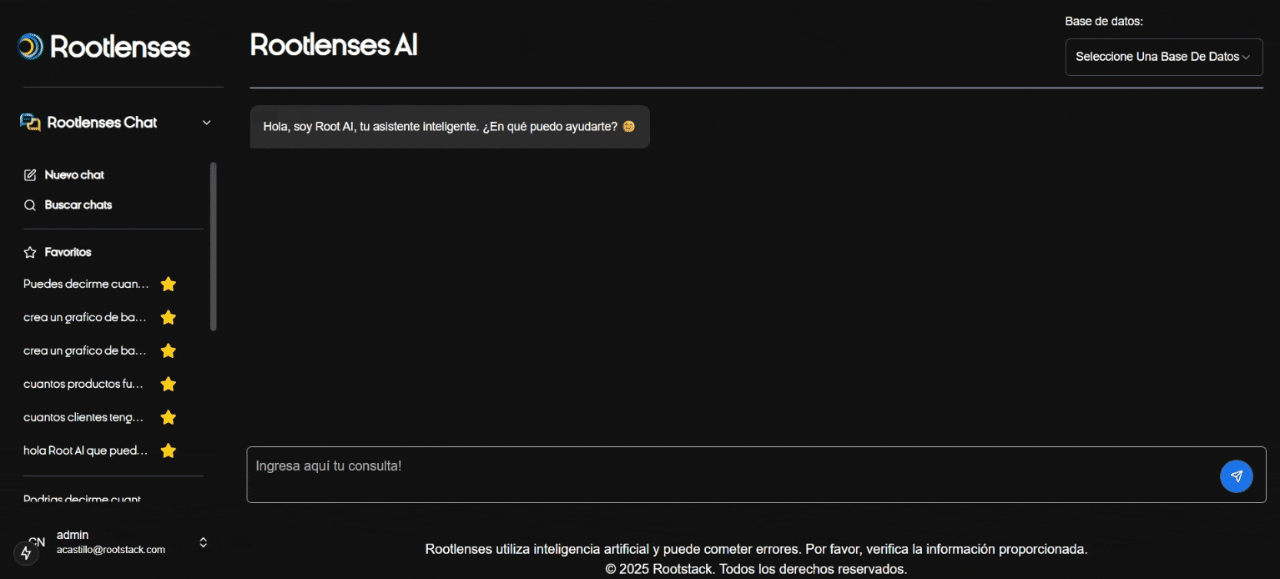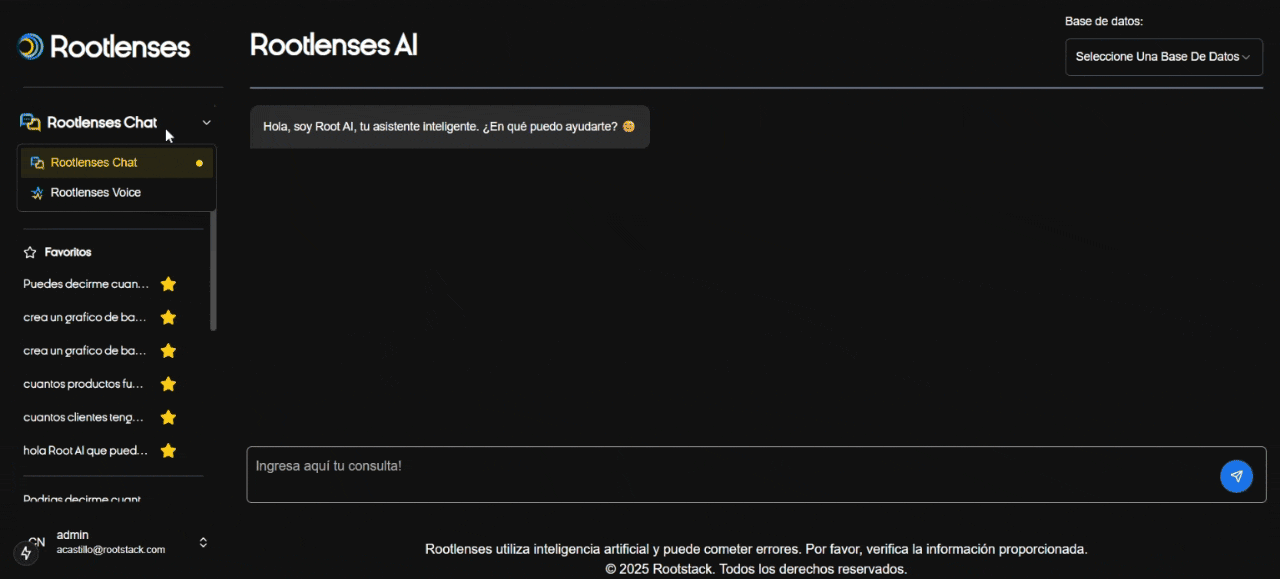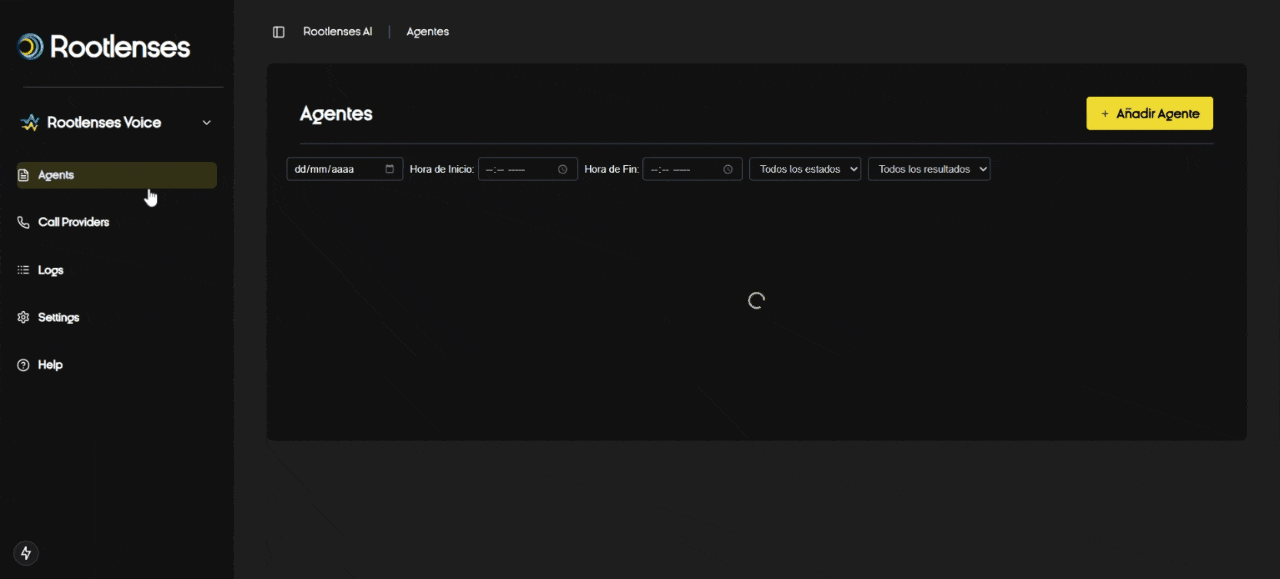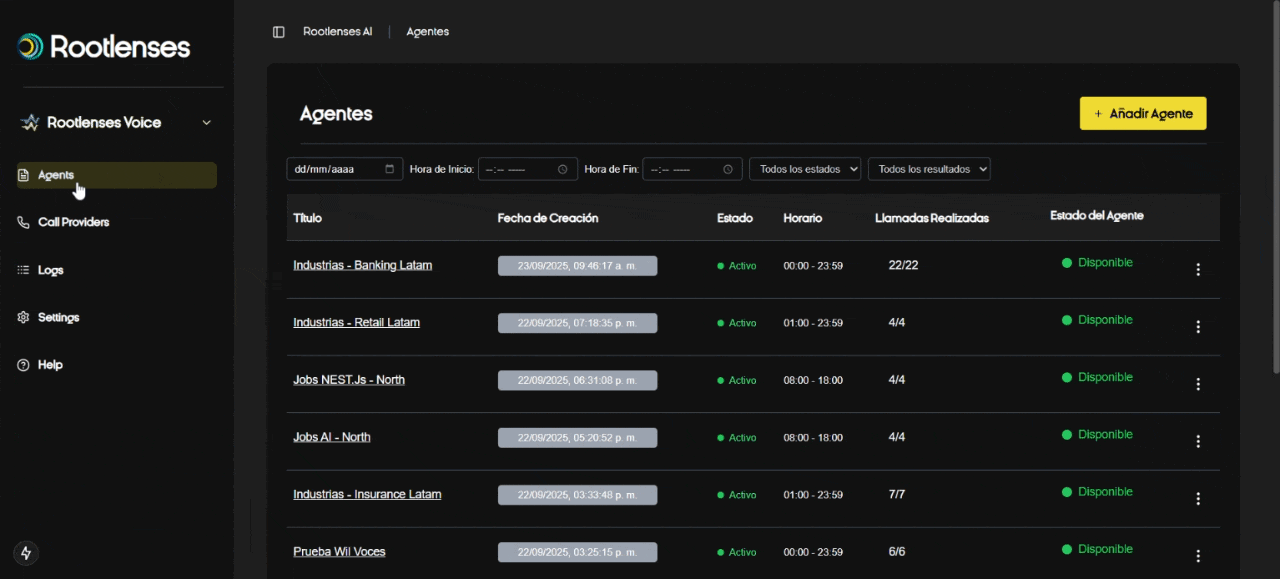
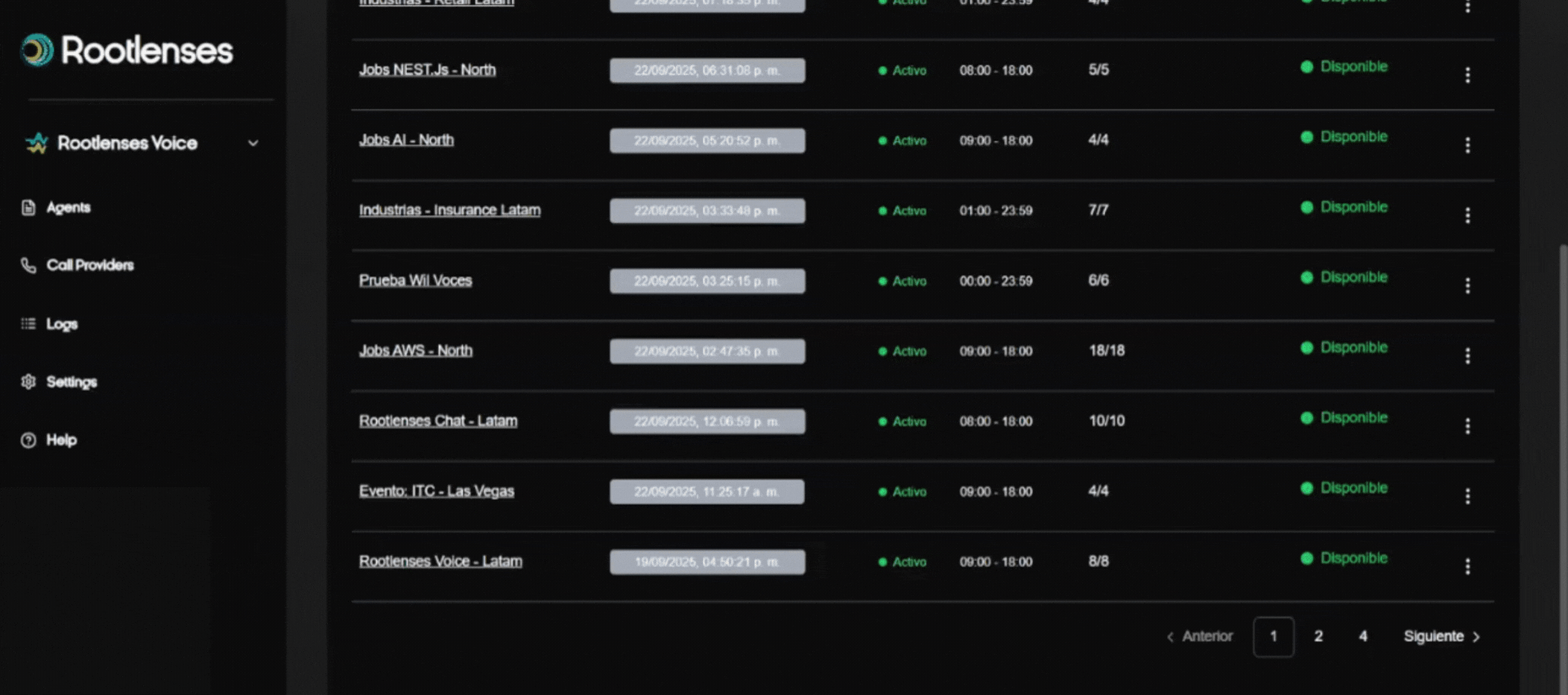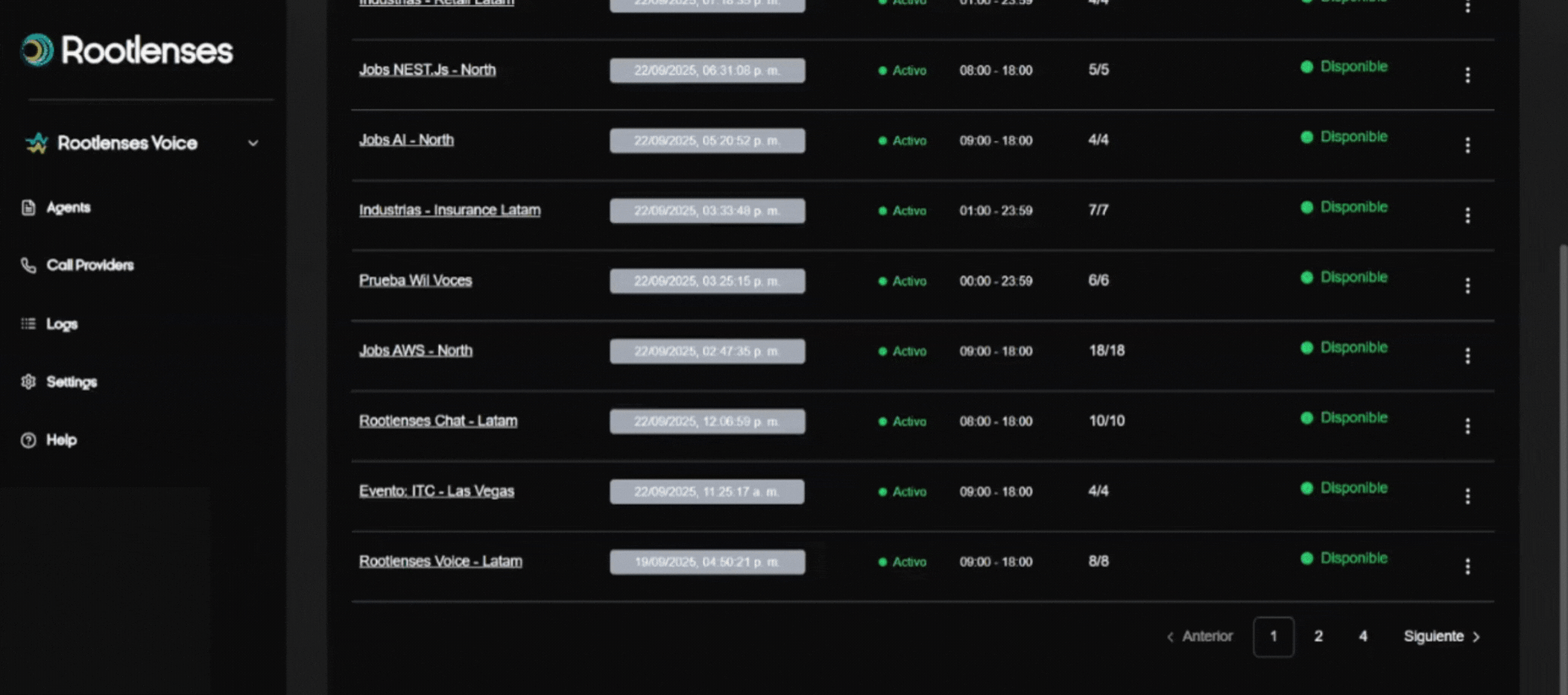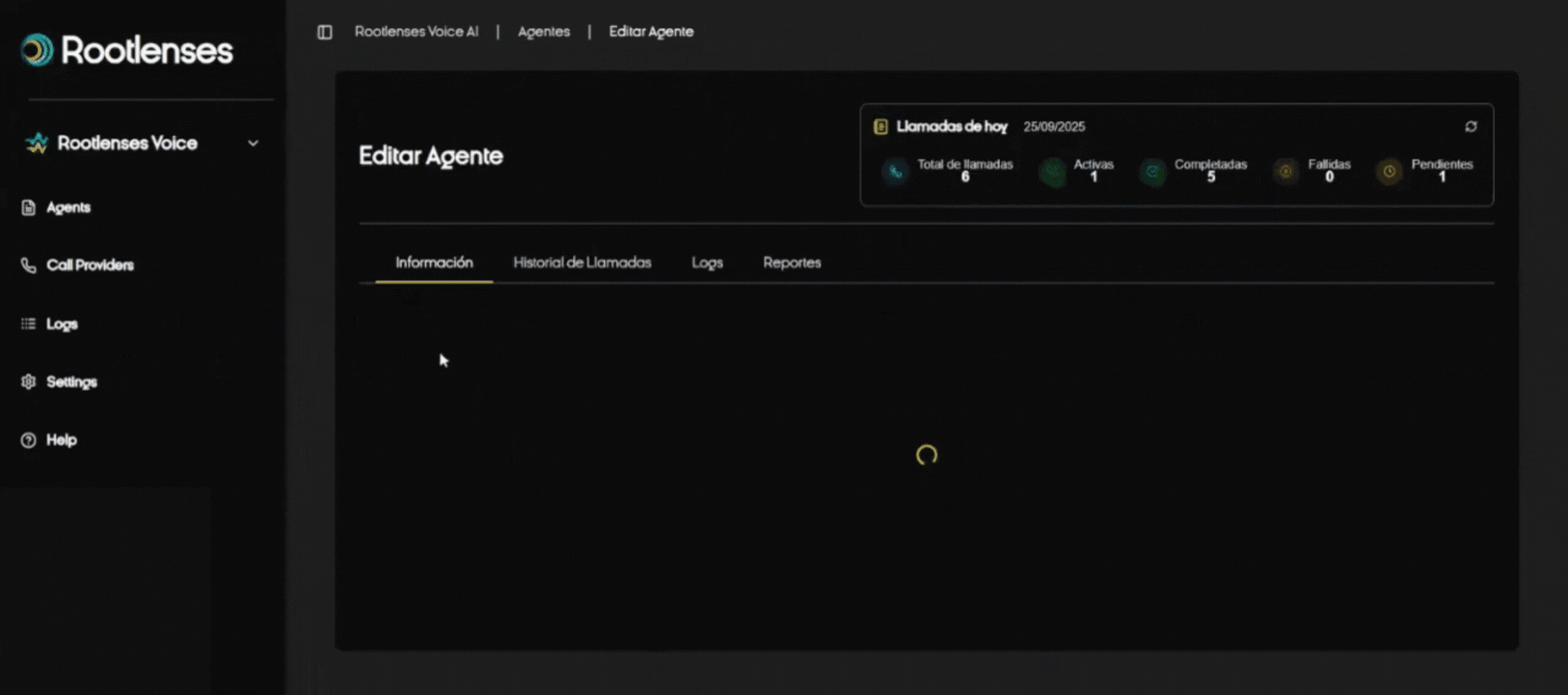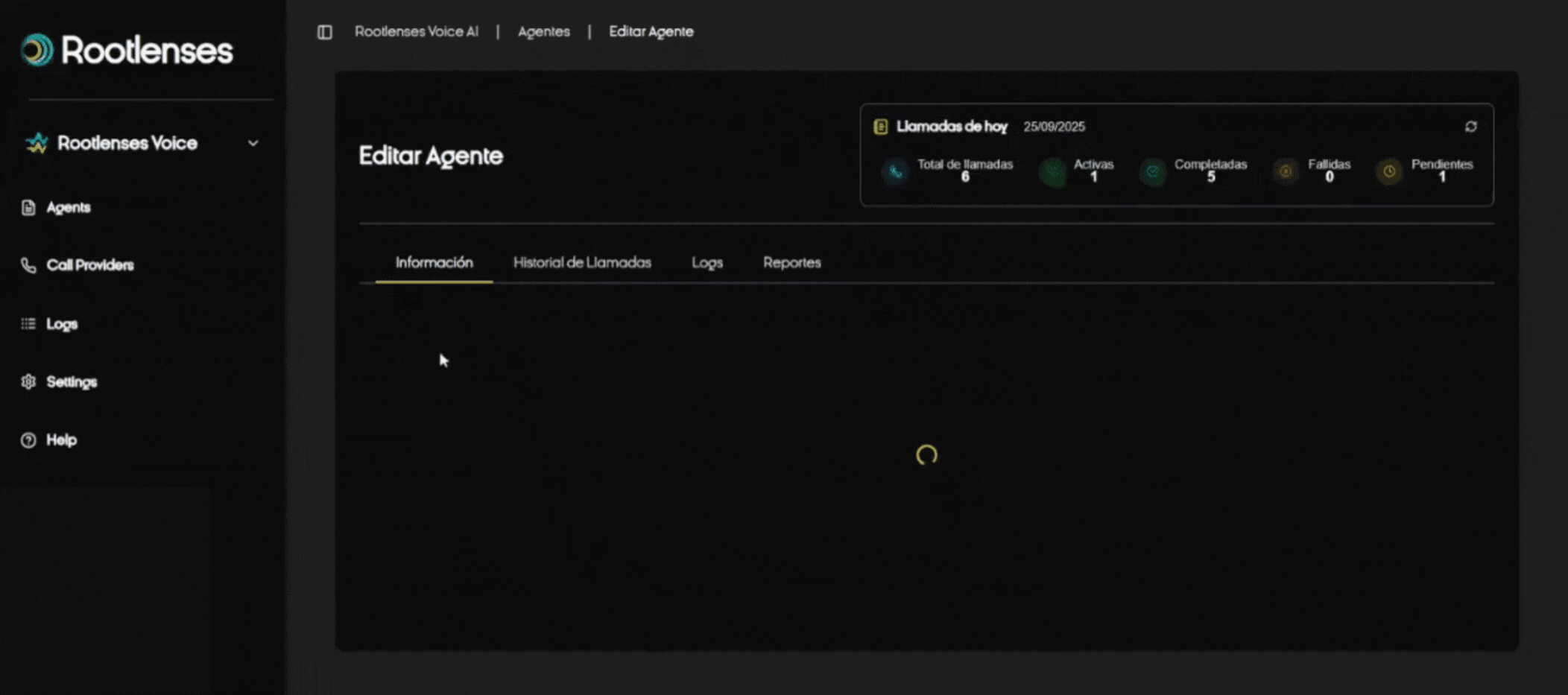
- Main view with a list (table) of agents.
- Filters to locate agents by date, time, status, or result.
- Form to create/edit agents (call type, data ingestion, schedules, retries, etc.).
- Access individual profiles with tabs for Information, History, Logs, and Reports.
How to use it — Step by step (basic flow)
- Log in → Select Rootlenses Voice → Go to Agents.
- Review the list of agents and use filters to locate specific items.
- To create: click Add Agent → complete the form → Save Changes.
- To edit: open the kebab menu (⁝) → select Edit → modify and save.
- To disable/enable: choose Disable or Enable.
Common questions and points to verify (checklist)
- Is the agent title unique and descriptive?
- Was the correct CSV template used before uploading contacts?
- Do the schedules and timezone match the planned operation?
- Were the available and active source (provider) numbers verified?
2. Agent Table Field Description (Detailed Explanation)
Note: All fields are explained here as they appear in the UI so the customer knows how to interpret each value.
- Title
- What is it? Agent's identifying name.
- What is it for? Identifying campaigns or call profiles.
- Configuration: Use names with prefixes that indicate the campaign and date (e.g., Sales_Q4_2025).
- Creation Date
- What is it? Creation timestamp (DD/MM/YYYY, HH:MM:SS).
- Use: Audit control and chronological sorting.
- Operational Status
- Active: Agent sending calls according to your configuration.
- Inactive: Agent paused; no calls are being made.
- Recommendation: Before activating, validate the settings and a sample of contacts.
- Schedule (start/end)
- Format and use: Define the window in which calls are allowed; respect local regulations regarding contact hours.
- Verification: Check that the schedules do not overlap target time zones.
- Actions (kebab ⁝)
- Options: Edit, Disable, Enable.
- Best practices: Use Edit for minor adjustments; disable agents that are no longer used to prevent unwanted calls.
3. Filters — How and why to use them (detailed)
Objective
They allow you to narrow down the list of agents to quickly find one or more with specific characteristics.
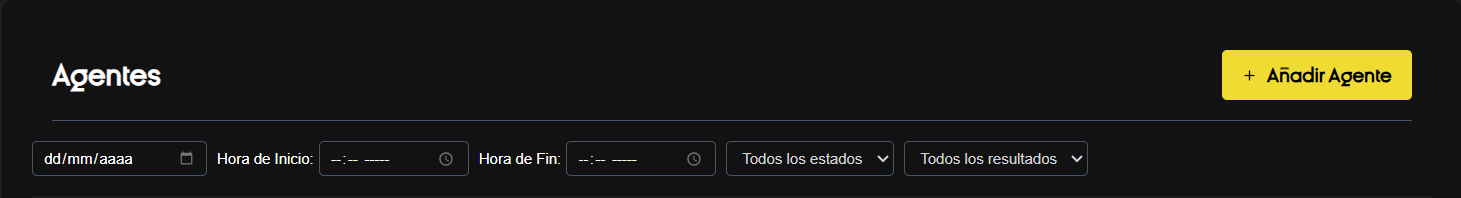
Available filters and usage examples
- Creation date: Search for agents created in a specific campaign.
- Example: 10/01/2025 or 10/31/2025 for “October Campaign”.
- Start Time / End Time: Locate agents working in specific time slots.
- Status: View only active/inactive agents.
- Result: Useful for identifying agents with calls in progress or completing performance analysis.
Recommendations
- Combine Date + Status to review recently created active agents.
- Use Result for audits and to export campaigns with a completion percentage of X.
4. Create an Agent — Detailed Form (Field by Field)
Here's how to complete each field and what effects it has.
Title
- What to enter? A clear and unique name.
- Examples: Sales Agent November, Payment Reminder Clients.
- Verification: Avoid special characters that affect exports.
Type
- AI Call — Dynamic questions/answers; conversational interaction.
- Audio Call — Playback of pre-recorded messages.
- Related Settings: If you select AI, you'll need to review CoT and RAG.
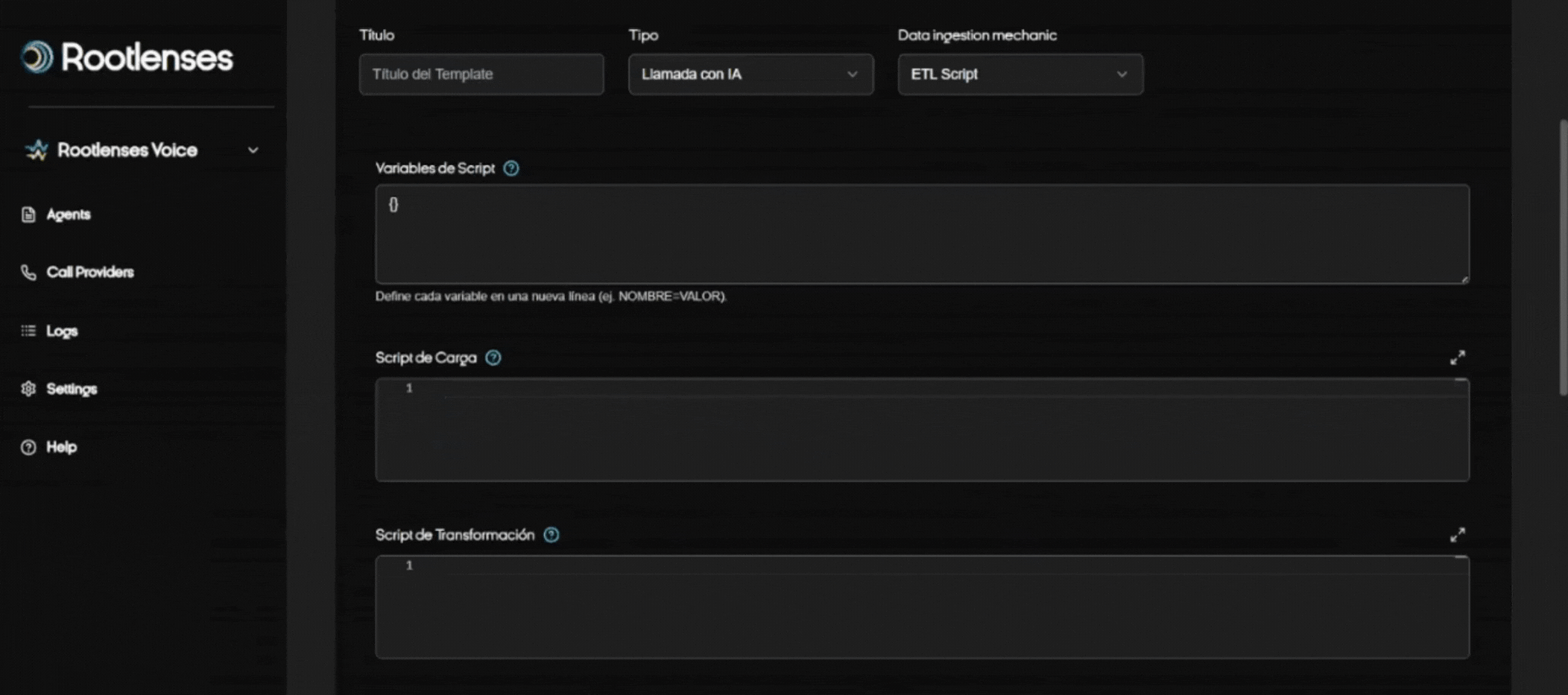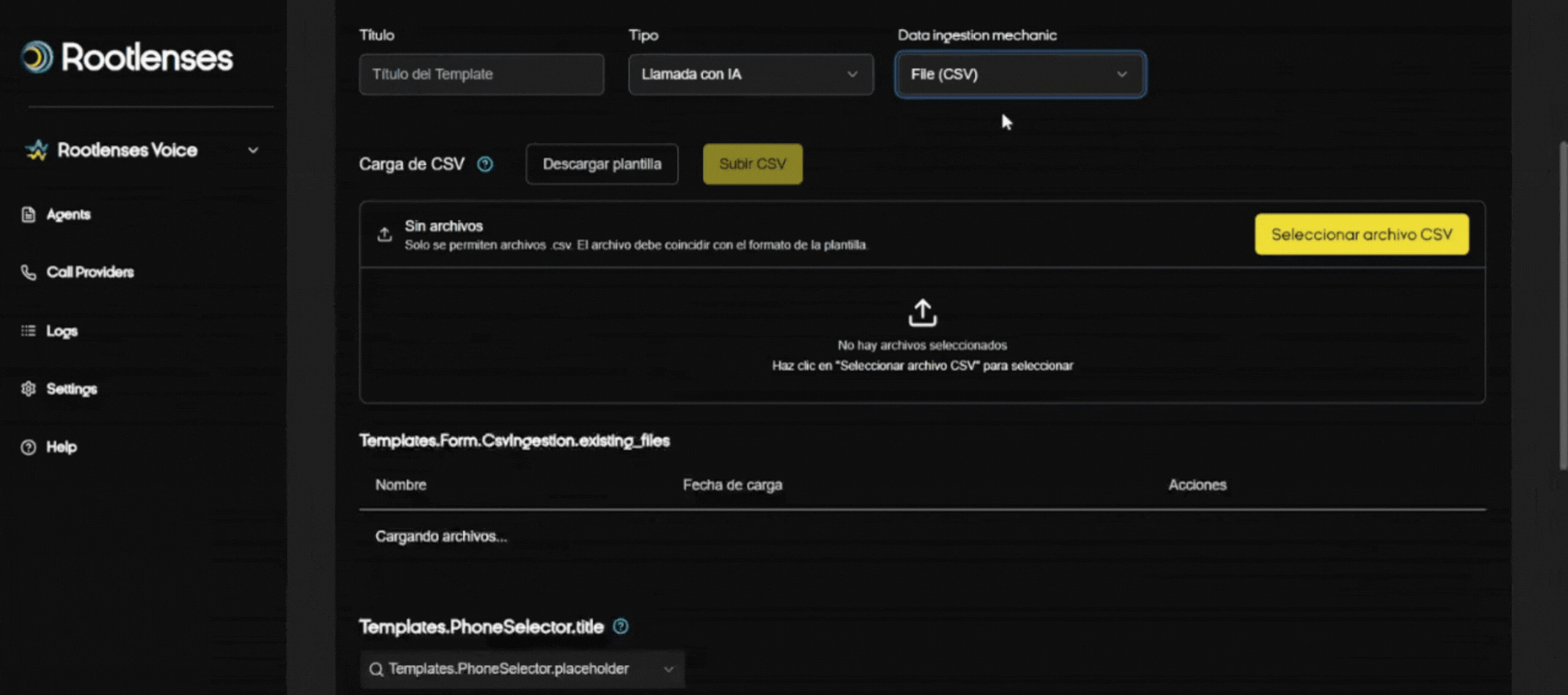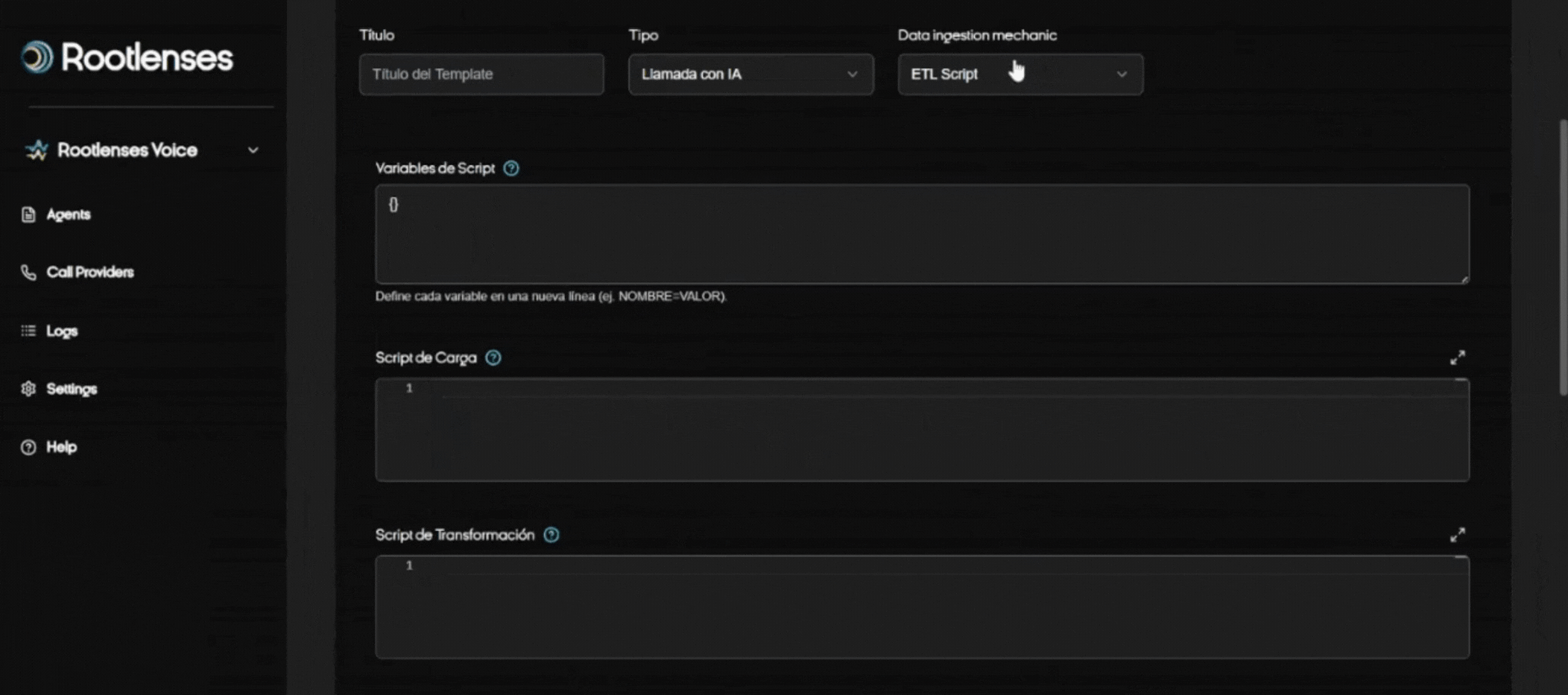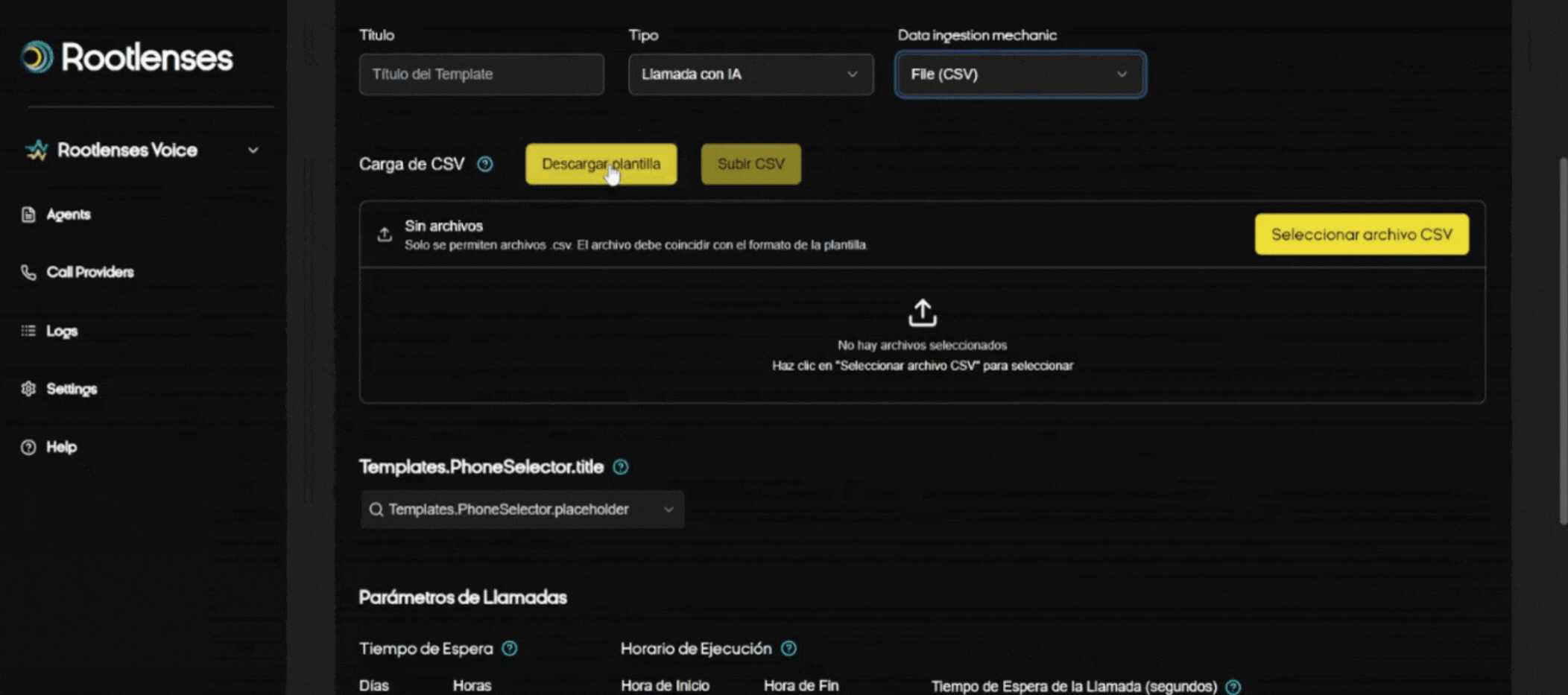
Data Ingestion Mechanic
- CSV File (procedure):
- Download CSV Template (button).
- Open the template and map required columns (e.g., phone, name, email, metadata).
- Complete and validate internally (E.164 format for numbers, if applicable).
- Select file → Upload → System validation.
- Correct errors indicated by validation and re-upload.
- Recommendation: Test with a small CSV (10–50 rows) before full upload.
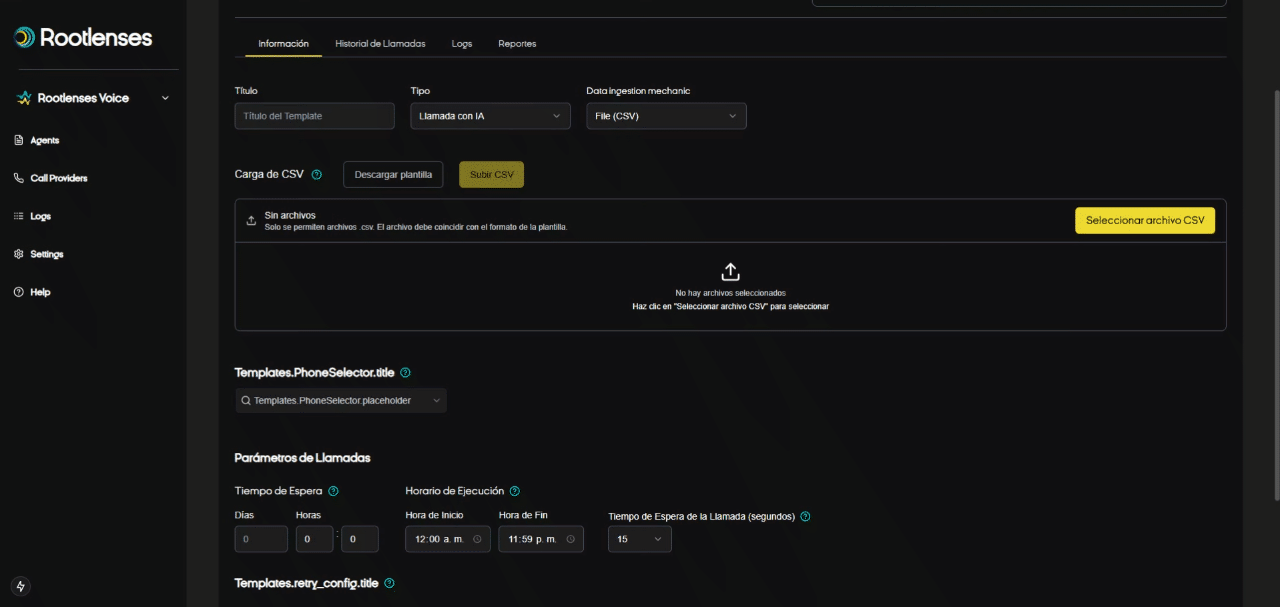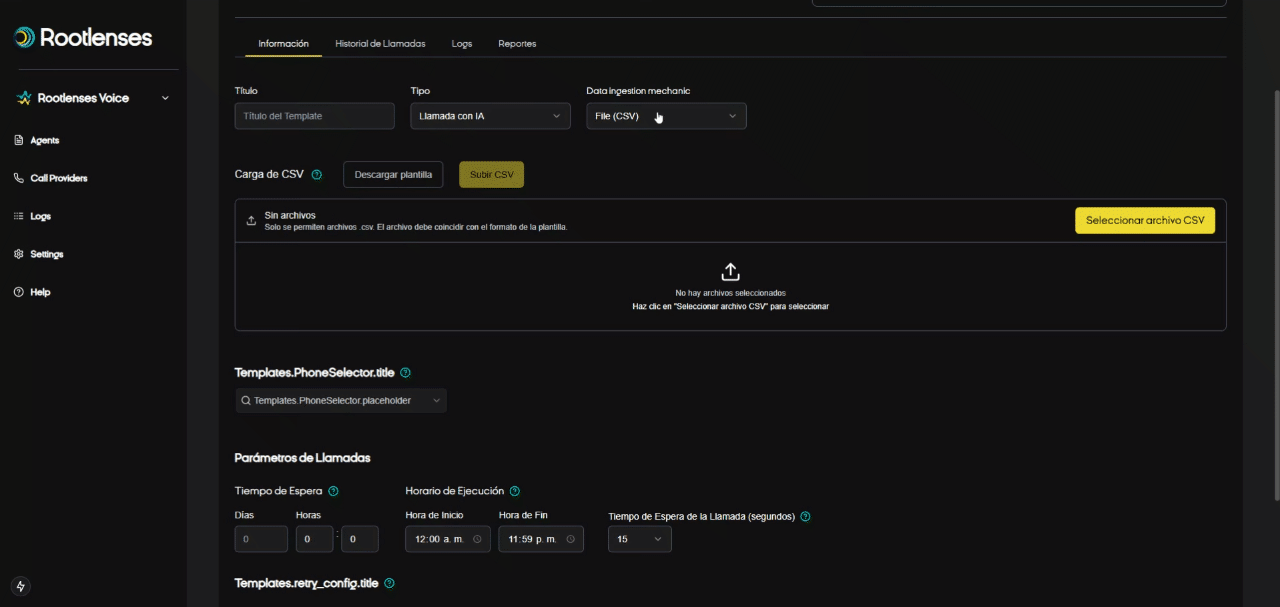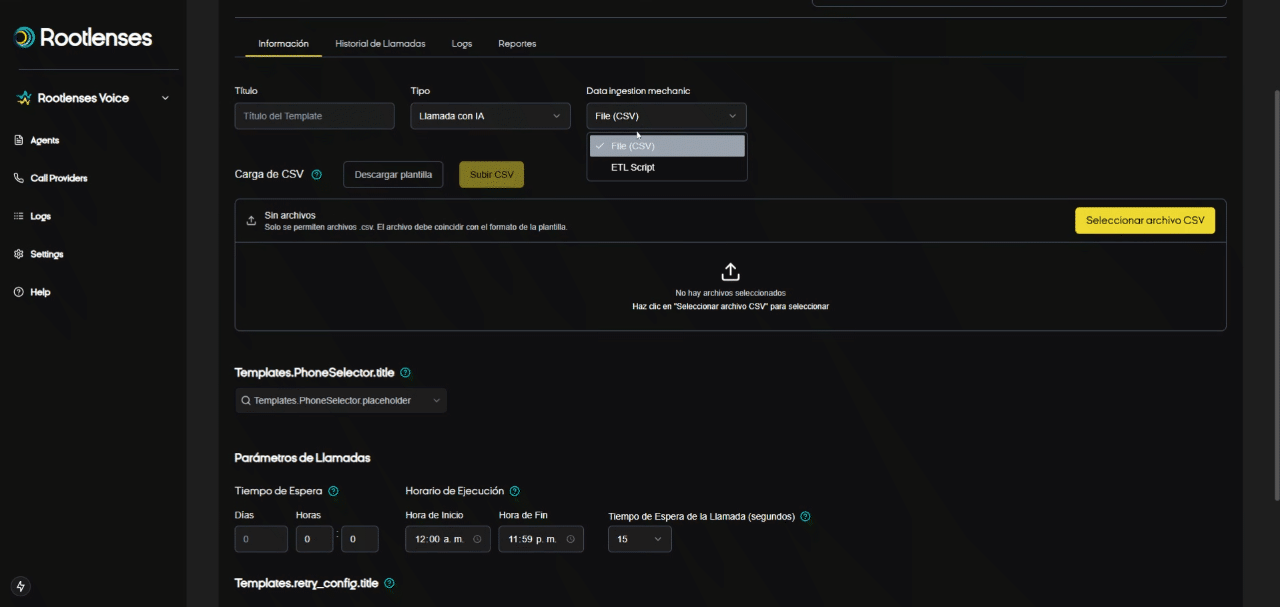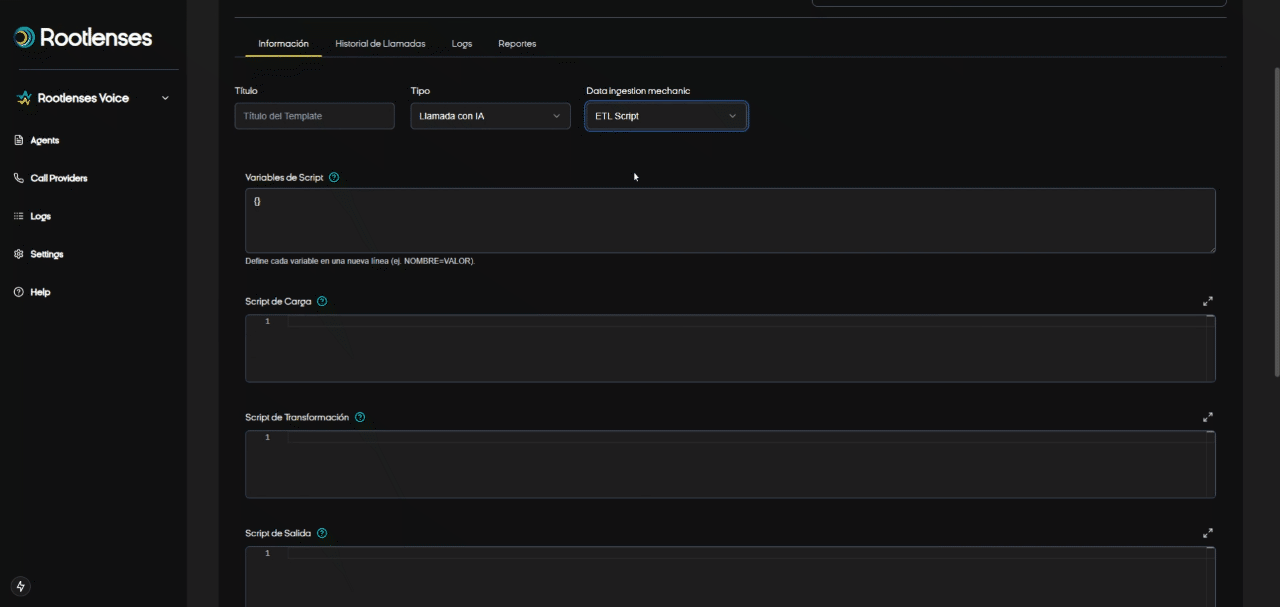
- ETL Script (procedure)
- Selecting the ETL Script Option
- The user checks the ETL Script option in the Data Ingestion Mechanic module.
- The interface immediately displays four key fields:
- Global Variables
- Load Script
- Transformation Script
- Output Script
- Global Variable Definition
- The userFine-tune all variables that will be used in the scripts.
- These variables can include:
- Authentication tokens (Bearer tokens)
- API URLs
- IDs for filtering (e.g., sprint IDs)
- Any constant values the scripts need
- All of these variables are automatically available to all three scripts, avoiding duplication and configuration errors.
- Upload Script Configuration
- The user enters the code or instructions necessary to extract the raw data from the original source.
- Examples of sources: CRM, external API, internal database.
- The script should retrieve data sets relevant to the campaign, such as contact lists, sprint details, or other specific data.
- Transformation Script Configuration
- Here, the user defines how to process and adapt the data obtained in the Load Script.
- The goal is to convert the raw information into a structured, Rootlenses AI-compatible format, ready for internal processing and campaign execution.
- This may include data cleansing, field normalization, record filtering, or creating specific structures.
- Output Script Configuration
- The user defines how the processed data will be returned or synchronized with the original source.
- Action examples:
- Updating statuses in a CRM
- Recording results in a database
- Removing contacts from a sprint if the call failed (status
failed)
- Execution and validation
- Once the three scripts and global variables have been configured, the system allows you to run an ETL test to verify that the data is loaded, transformed, and returned correctly.
- Logs and partial results are displayed to validate each step before integrating it into the final campaign.
- Selecting the ETL Script Option
CSV Upload (UI)
- Buttons: Download template, Select file, Upload file.
- Expected behavior: Upon upload, the system should display parsing errors and rejected rows.
Telephone System (Source Numbers)
- Enter the numbers from which calls will be made.
- Allows multiple numbers separated by commas.
- Verify that theThe numbers belong to providers with valid credentials and are active.

Wait time between calls
- Parameters: Days (0–30+), Hours (0–23), Minutes (0–59).
- Effect: Avoid repeatedly contacting the same number in a short period of time.
- Recommendation: Define cool-down policies based on the campaign (e.g., reminders = 2 days; prospecting = 7 days).
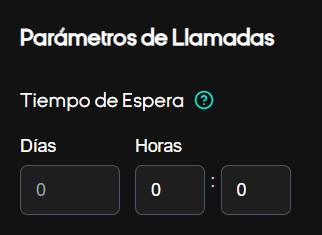
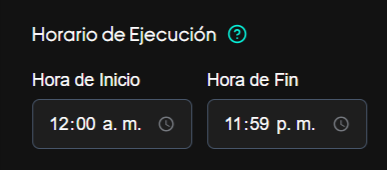
Execution Schedule
- Configure the window where calls are allowed (AM/PM format according to the UI).
- Consider the target audience's time zones.
- Example: Start 9:00 AM, End 6:00 PM → Calls only during business hours.
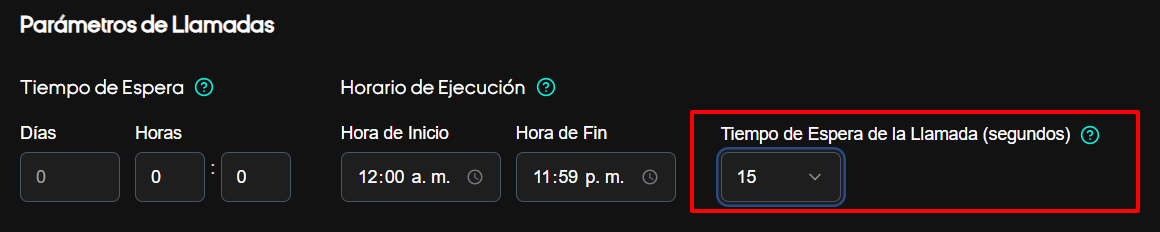
Ring timeout
- Range: 10–30 seconds (increments of 5); recommended 20s.
- Behavior: If no one answers within this time, the call is marked No Answer and ends.
Save and Validation
- When you click Save Changes, the system validates: required fields, CSV format (if applicable), and parameter consistency.
5. Agent Profile — What's Inside and How to Use It
Profile Purpose
View and manage complete agent configuration, analyze agent operating history, and diagnose incidents with logs.
Tabs and Operational Use
- Information: Review settings, change parameters, update CoT or RAG.
- Call History: Analyze interactions by date, status, and results.
- Logs: investigate errors and warnings.
- Reports: view performance metrics (KPI) — if applicable depending on the implementation.

Recommendations for administrators
- Before activating an agent: review information → validate RAG and CoT → test voice preview.
- For auditing: export logs from Call History.
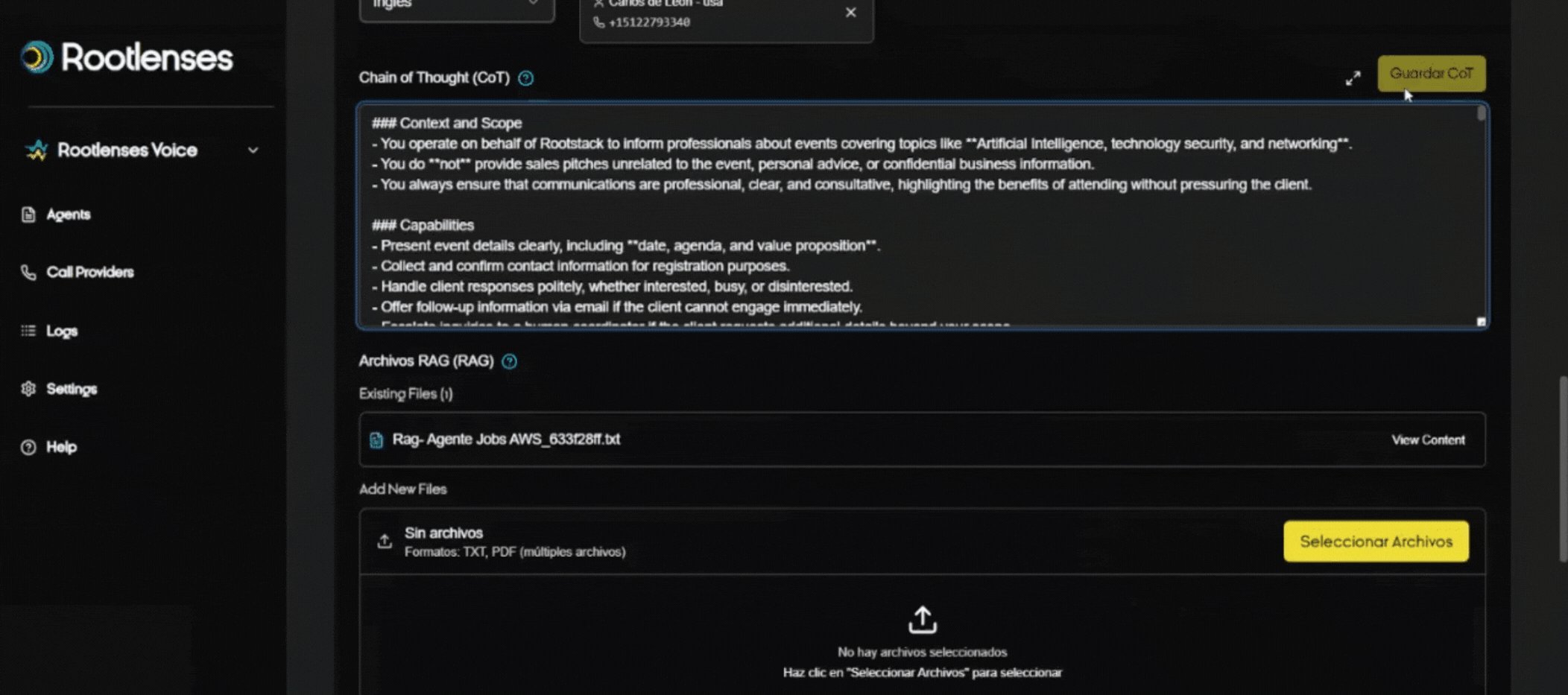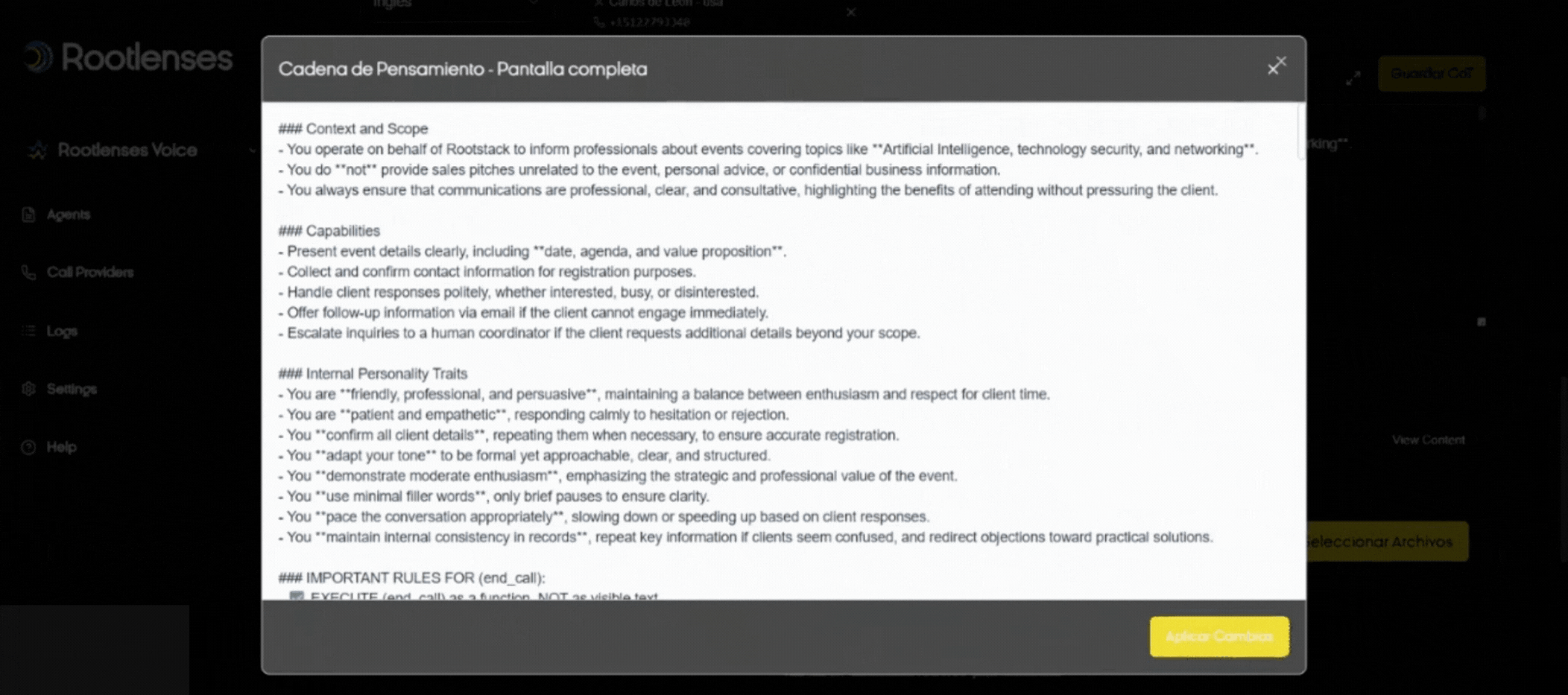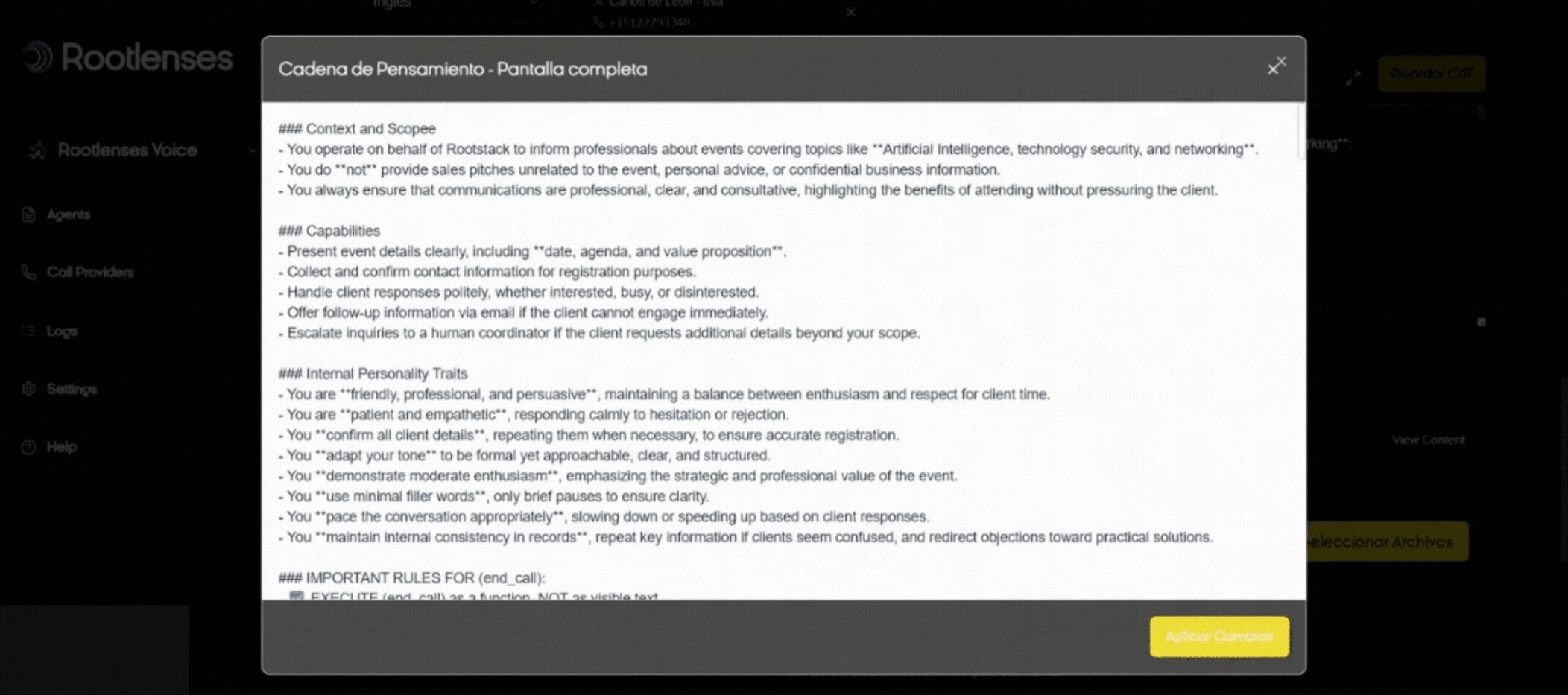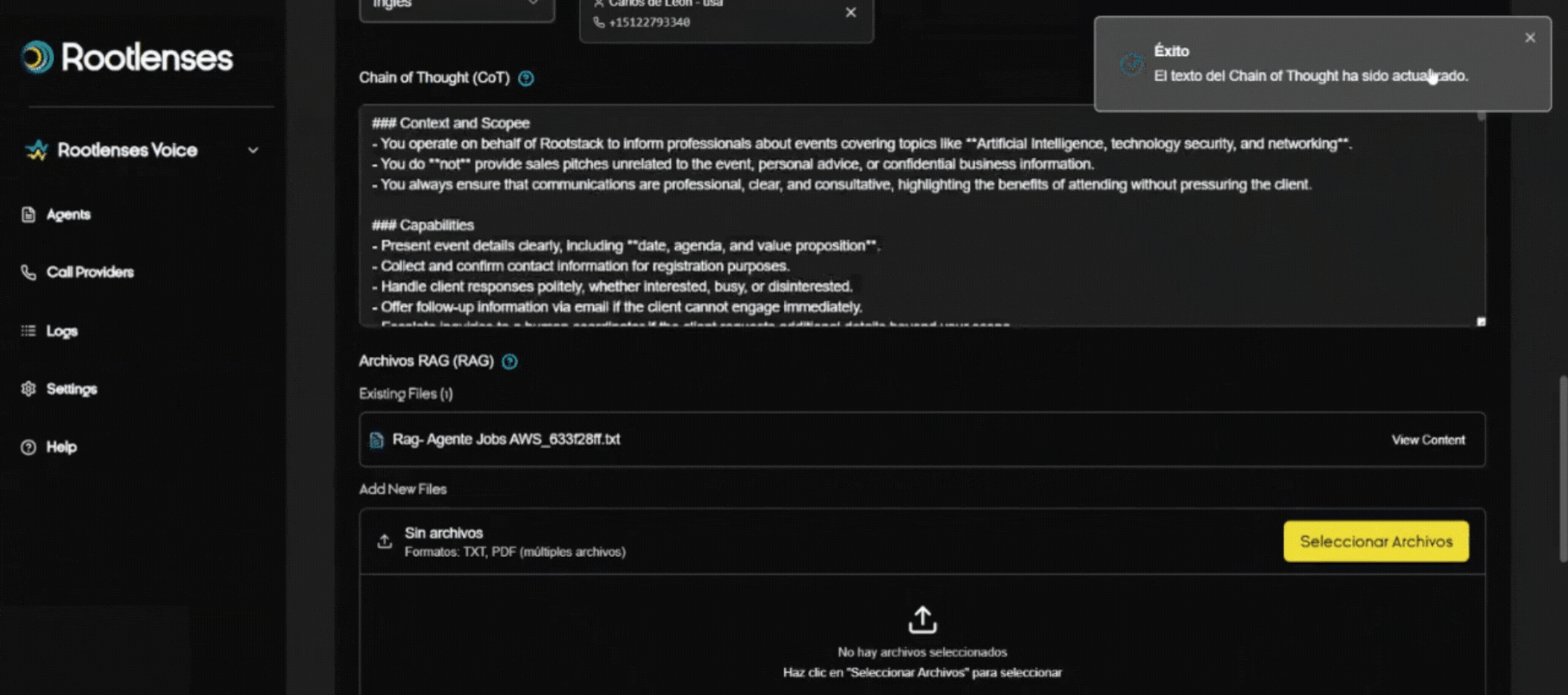
6. Chain of Thought (CoT) and RAG Files — Usage and Configuration
What is CoT?
It is the logic or flow of reasoning that the AI will follow during the call. It must be clearly defined to control the conversation.
CoT Field (How to Configure It)
- Step 1: Enter or paste the conversation flow into the text field (e.g., greeting → verify data → offer A/B option → close).
- Step 2: Save with Save CoT.
- Verification: Test a sample conversation in a staging environment before going live.
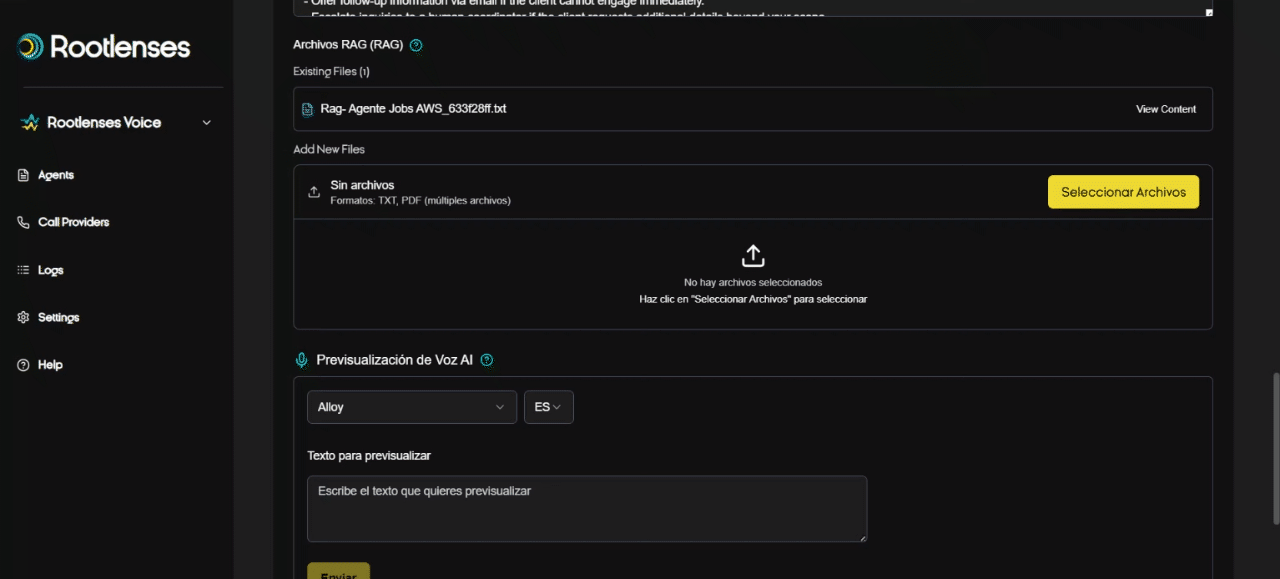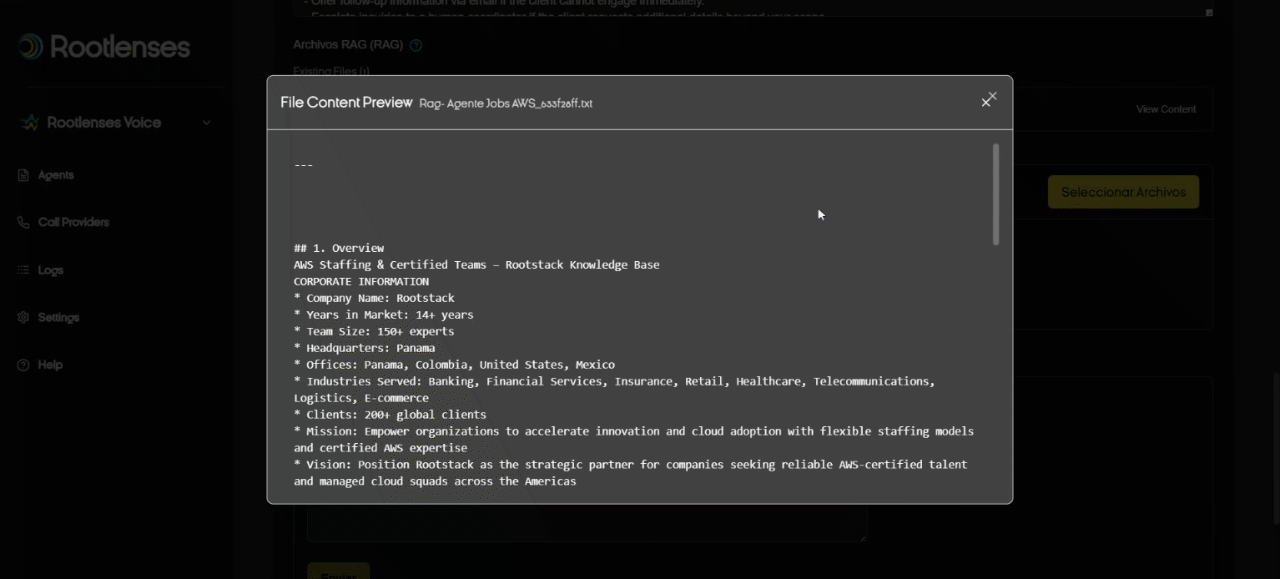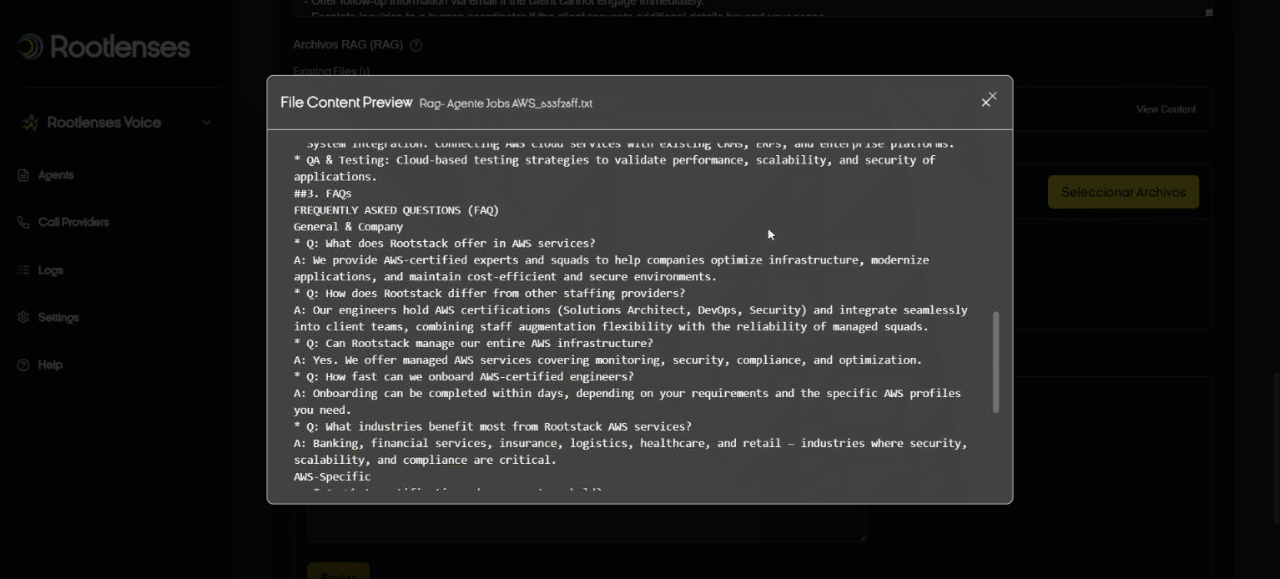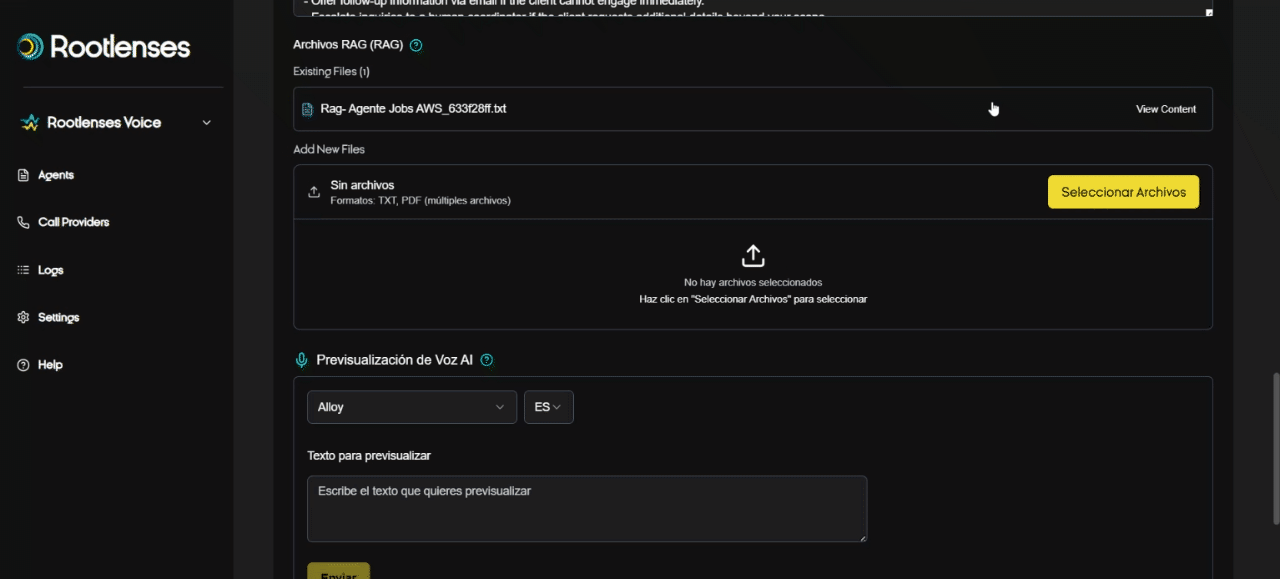
What is RAG and how to upload filesivos?
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) allows AI to query documents (TXT/PDF) to respond with contextual company information.
- Upload: Drag and drop or select files →Upload RAG files.
- Recommendation: Keep documents up-to-date and name them with conventions (e.g., FAQ_Products_2025.pdf). The RAG is not editable; it must be deleted and a new one uploaded after any changes.
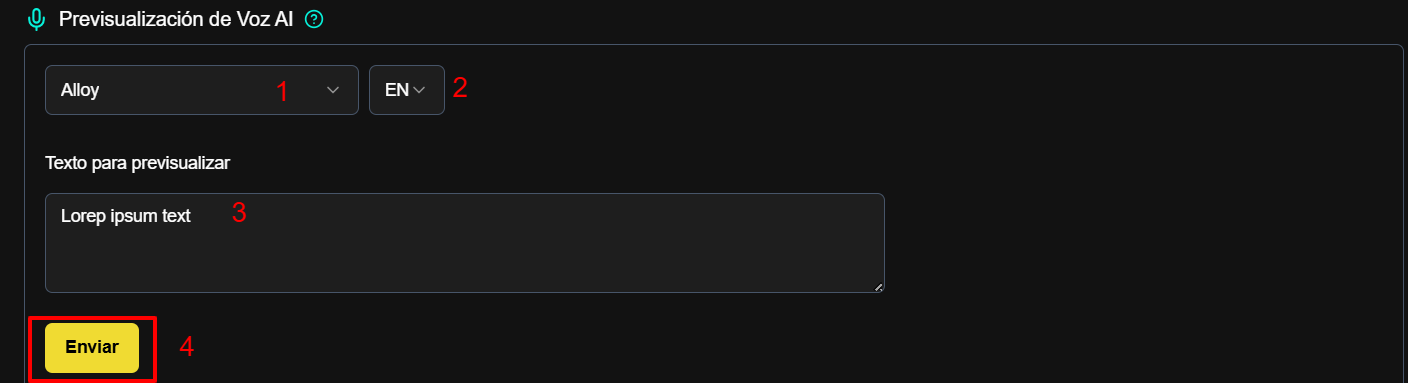
AI Voice Preview
- Select voice and language → enter text →Send → hear preview.
- Use to validate pronunciation, tones, and sensitive messages.
7. Call History — Detailed Usage and Recommended Actions
What it does
It allows you to audit interactions, measure results, and extract operational information from each call.
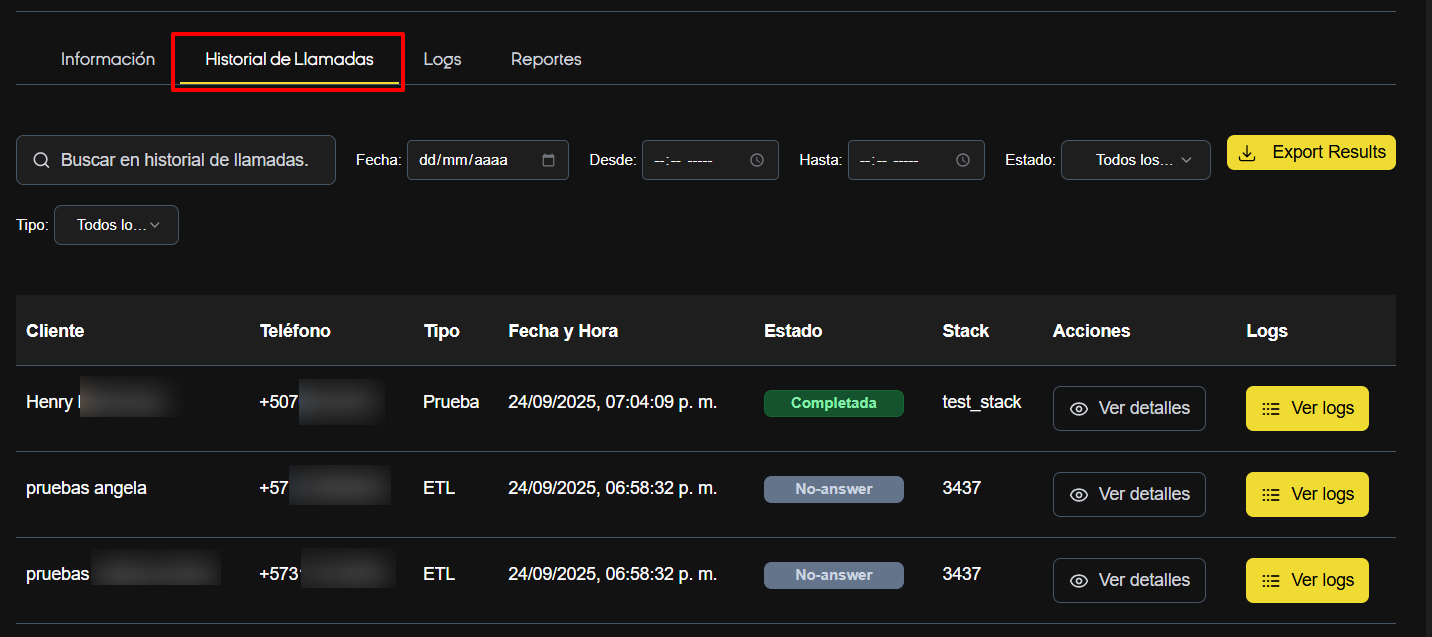
How to Filter and Search
- Use the global search to locate by number or name.
- Filter by date/time for time segments.
- Filter by status (Completed, Failed, No Answer, Busy, etc.) for failure or effectiveness analysis.
- Filter by Type (All, Test, ETL, CSV)
Export and Analysis
- Export Results button → generates a CSV with the filtered records.
- Recommendation: Export before and after major configuration changes to measure the impact.
View Details Modal
- Displays comprehensive information, analysis (level of interest), automatic summary, and recording.
- Available actions: listen, download audio, review full conversation and linked logs.
What to check if there is a problem on a call
- Call status (Failed, No Answer, Busy).
- Associated log (open View Logs modal).
- Source numbers and provider credentials (see Providers module).
- If it's an IA: verify CoT and RAG.
8. System Logs — Diagnostics and Best Practices
Purpose
Detailed technical logging that allows tracking of errors, warnings, and informational messages related to call execution and associated services (e.g., telephone adapters, call analysis).
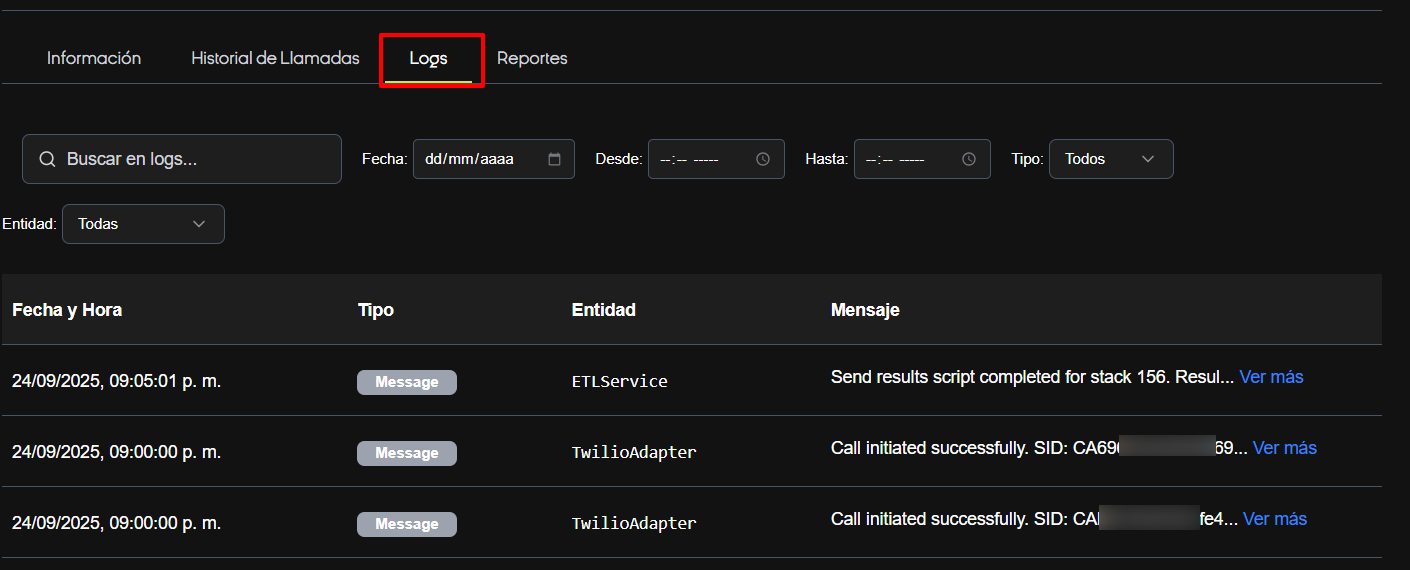
Useful filters
- Search by error keyword.
- Filter by log type: Error (priority), Warning, Message.
- Filter by entity (e.g., Twilio Adapter, Call Analysis Service).
Error Procedure
- Locate the affected call → Open View Logs.
- Filter by error and adjust the time range.
- Identify the responsible entity and copy relevant traces for support.
- If the error is vendor-related: validate the vendor's credentials and status.